Thyroid Health: Understanding the Key to Your Hormone Balance
The thyroid gland, located in the front of your neck, plays an important role in your metabolism, energy levels, and overall hormonal balance. Hormones are chemical messengers in our body that regulate its homeostasis. The thyroid gland produces hormones – triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) – that regulate your body’s energy use, from your heart rate to the amount of calories you intake and use , everything is affected if thyroid is involved
Generalized thyroid disease
- Hypothyroidism: When your thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones it leads to fatigue, weight gain, obesity, constipation and depression. The condition can be effectively managed with medication and lifestyle changes.
- Hyperthyroidism: An overactive thyroid gland produces too many hormones, causing symptoms such as weight loss, increased heart rate, tremors and nervousness. Treatment options include medications, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery.
- Thyroid nodules: Possible nodules on the thyroid gland. Most are harmless, but some may need additional screening to detect cancer.
- Thyroid cancer: Although rare, thyroid cancer is treatable, especially if caught early. Routine screening and diagnostic testing are important for those at risk.
Why should you see an endocrinologist?
An endocrinologist specializes in diagnosing and treating conditions related to the body’s hormonal system, such diabetes, obesity, growth and reproductive disorders along with thyroid disorders. Whether you’re dealing with an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism), an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism), or more complex conditions like thyroid nodules or cancer, an endocrinologist is your go-to expert.
Personalized Diagnosis and Treatment
Endocrinologists use detailed tests such as blood work to measure hormone levels and imaging techniques like ultrasounds to evaluate the structure of your thyroid. Based on these results, they create a personalized treatment plan, which may include medications, lifestyle changes, or advanced treatments like radioactive iodine or surgery, depending on the condition.
Ongoing Monitoring
Because thyroid disorders can change over time, your endocrinologist will provide continuous care, adjusting your treatment as needed. This helps ensure your hormone levels remain balanced, and symptoms are effectively managed.
Type of Thyroid
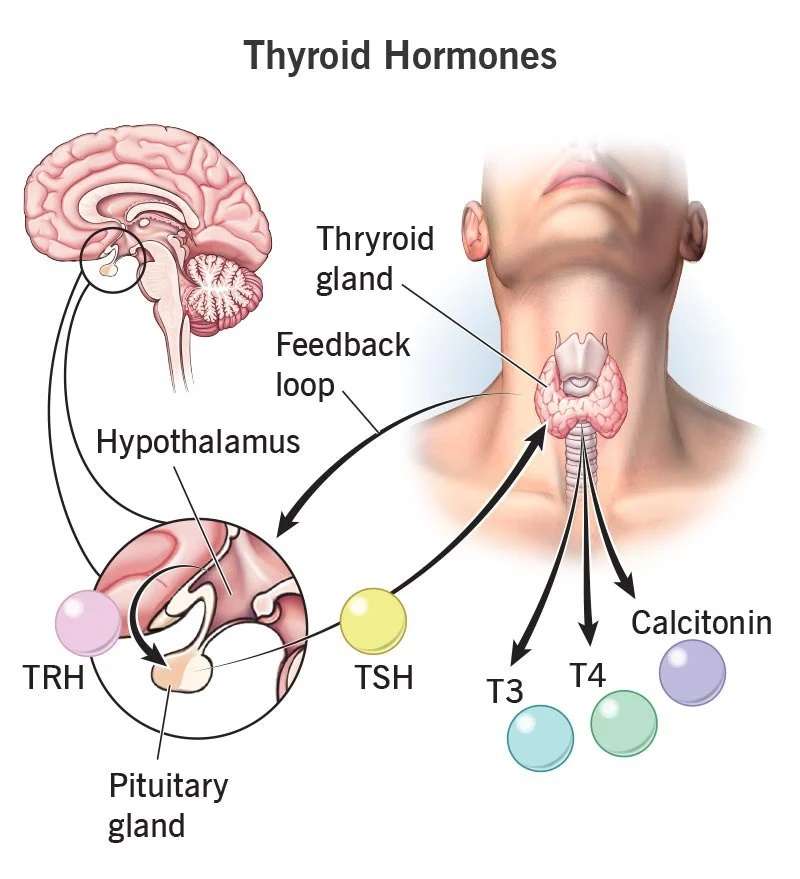 1. Thyroid Function:
1. Thyroid Function:
- The thyroid gland, located in the neck, produces hormones (T3 and T4) that regulate metabolism, energy production, and body temperature.
- Hypothyroidism:
- Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid produces insufficient hormones, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and sensitivity to cold.
- Hyperthyroidism:
- Hyperthyroidism results from an overactive thyroid, leading to excessive hormone production, causing symptoms like weight loss, rapid heart rate, and heat intolerance.
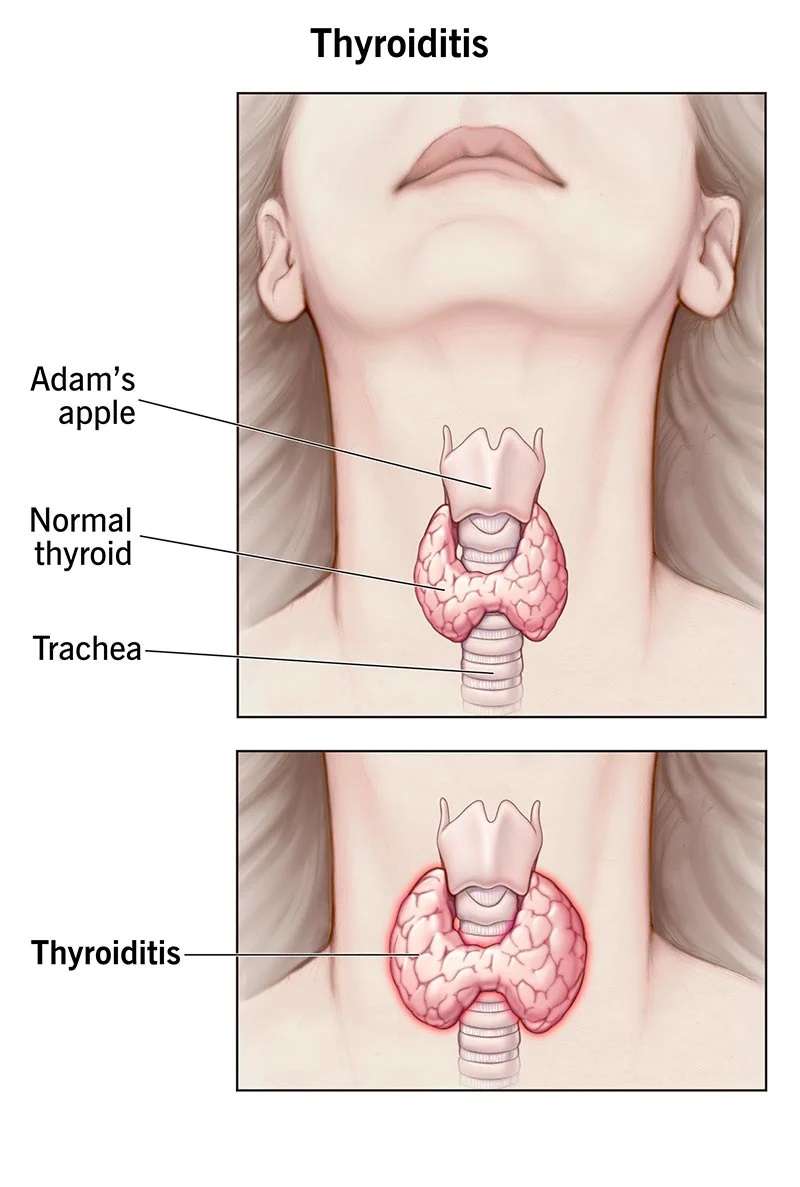
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis:
- Hashimoto’s is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the thyroid, causing hypothyroidism and often resulting in an enlarged thyroid (goiter).
- Graves’ Disease:
- Graves’ disease is an autoimmune condition causing hyperthyroidism, characterized by bulging eyes (exophthalmos), weight loss, and an enlarged thyroid. It is often associated with antibodies stimulating excessive hormone production.
