Pituitary
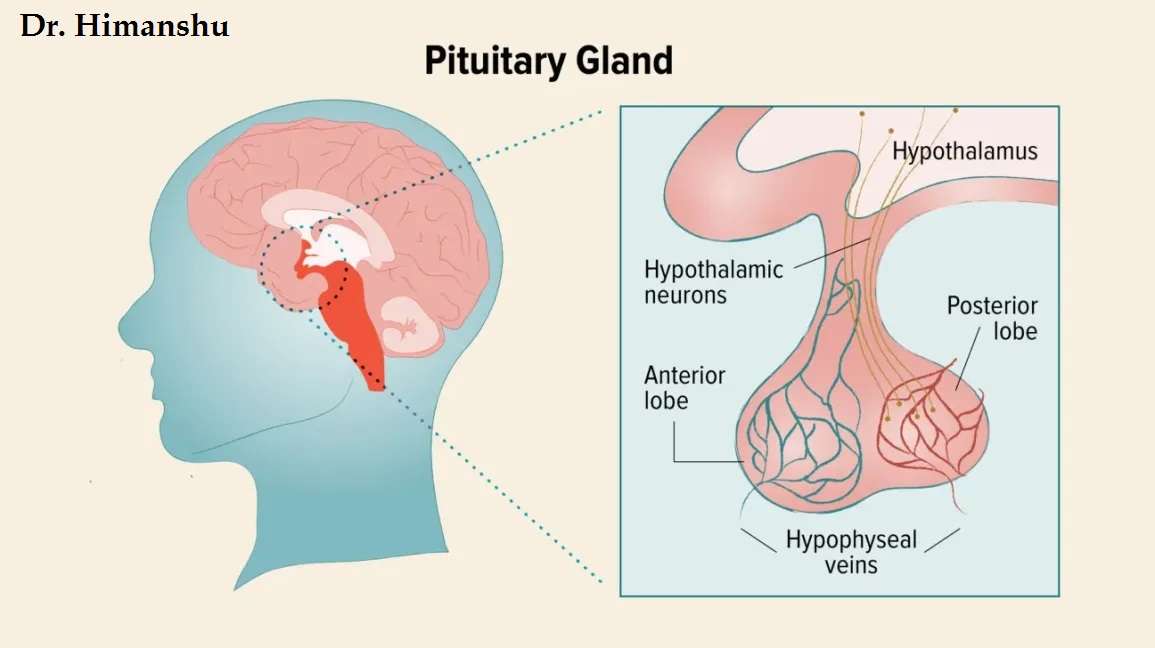
What is the Pituitary Gland?
The pituitary gland, often called the “master gland,” is a small, pea-sized organ located at the base of the brain. Despite its size, it plays a crucial role in regulating various hormonal functions throughout the body, making it essential for overall health and well-being.
Hormone Secretion
The pituitary gland is divided into two lobes:
Anterior Pituitary (Adenohypophysis)
This lobe is responsible for secreting several important hormones, including:
- Growth Hormone (GH): Essential for growth and metabolism.
- Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH): Regulates thyroid function.
- Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH): Stimulates the adrenal glands to produce cortisol.
Posterior Pituitary (Neurohypophysis)
This lobe releases:
- Oxytocin: Plays a key role in childbirth and bonding.
- Vasopressin (Antidiuretic Hormone): Regulates water balance in the body.
Feedback Mechanisms
The secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland is tightly regulated by feedback mechanisms involving the hypothalamus and other target glands. This intricate system ensures a finely tuned balance of hormones, maintaining optimal health.
Pituitary Disorders
 Pituitary Adenomas
Pituitary Adenomas
Pituitary adenomas are common benign tumors that can develop in the pituitary gland. These tumors can disrupt normal horm
one production and lead to various conditions, including:
- Acromegaly: Excess growth hormone causing enlarged bones and tissues.
- Cushing’s Disease: Overproduction of cortisol due to ACTH-secreting tumors.
- Hyperprolactinemia: Elevated levels of prolactin, affecting reproductive health.
Hypopituitarism
Hypopituitarism occurs when the pituitary gland fails to produce one or more hormones adequately. This condition can result from tumors, trauma, or other disorders, leading to symptoms such as:
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Hormonal deficiencies impacting various bodily functions
How an Endocrinologist Can Help
If you suspect a pituitary disorder, consulting an endocrinologist is crucial. Endocrinologists specialize in diagnosing and treating hormonal imbalances and related disorders. They can:
- Conduct Comprehensive Evaluations: Through blood tests and imaging studies, they can assess hormone levels and identify any abnormalities in the pituitary gland.
- Develop Tailored Treatment Plans: Based on your specific condition, they can create a treatment plan that may include medications, hormone replacement therapy, or referral for surgical evaluation if necessary.
- Provide Ongoing Monitoring: Regular follow-ups to monitor hormone levels and adjust treatment as needed ensure optimal management of your condition.
