Hormonal Health: Balance – The Elusive Key to Your Body’s Well Being

Hormones are chemical substances that are produced in the gland and are involved in controlling most functions in the body includes metabolism, growth, mood swings and reproductive system. Lifestyle diseases and all sort of complications are always associated with hormonal imbalance in the human body. They are physicians who major in identification and treatment of conditions in the endocrine glands that synthesize, discharge and manage hormones.
Common Hormonal Disorders
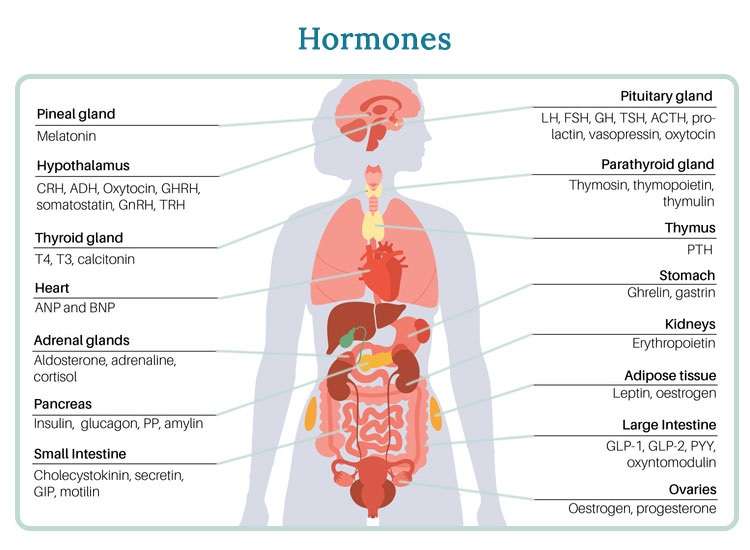 Thyroid Disorders: It secretes hormones that regulate metabolism, energy level and heat production in the body. Some diseases such as hypothyroidism (low hormone concentration in the body) and hyperthyroidism (high hormone concentration in the body) may affect these processes.
Thyroid Disorders: It secretes hormones that regulate metabolism, energy level and heat production in the body. Some diseases such as hypothyroidism (low hormone concentration in the body) and hyperthyroidism (high hormone concentration in the body) may affect these processes.
Diabetes: Insulin which is a hormone secreted by the pancreas, has a role to play in the blood sugar levels. Diabetes is a medical condition in which the body cannot produce sufficient amount of insulin or the insulin that is released in the body does not work as expected and blood glucose level rises.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): A state of bustle in women that is characterized by menstrual abnormalities, face and hairs growth and difficulty in conceiving. PCOS is associated with Insulin resistance and raised androgens, the male sex hormones, and an increase infat distribution.
Adrenal Disorders: The adrenal glands also secrete hormones to deal with stress, and control metabolism in the body. Some diseases are associated with failure of the necessary amounts of hormones to be produced, for example Addison’s disease or Cushing’s syndrome, pheochromocytoma and conns disease.
Growth Disorders: Other disorders associated with growth hormone include; The Growth hormone deficiency: it is characterized by absence/low growth hormone in children results in poor height growth
Puberty and Reproductive Disorders: both early and delayed development of sexual characteristics in females and males is usually a result of imbalance of reproductive hormone which can be effectively managed by an endocrinologist.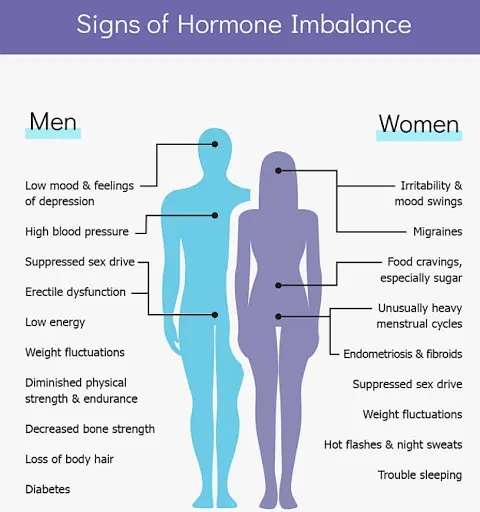
Pituitary Disorders – The pituitary gland, often referred to as the “master gland It plays a central role in regulating various hormonal functions throughout the body. Disorders of pituitary include prolactinoma, acromegaly, crushing’s disease and hypopituitarism
Parathyroid Disorders – Parathyroid hormone is essential for maintain calcium levels in the body. disorders of parathyroid gland can cause high or low calcium levels leading to weakness of bones, arrythmia etc.
Osteoporosis – Since osteoporosis can develop without any obvious symptoms, it is up to endocrinologists to spot often overlooked signs of bone loss and conduct research to improve understanding of osteoporosis and other bone diseases.
Gender affirmation hormone replacement – Endocrinologists play a key role in gender-affirming hormone replacement therapy (GAHT) for transgender and gender non-binary people by providing hormone therapy consultations and discuss the risks and benefits of starting treatment
Ways on How an Endocrinologist Can Help
Endocrinologist are specialized in diagnosing hormonal disorders and getting additional ways to deal with the abnormalities in the body. They offer:
Comprehensive Testing: Through lab tests like the blood tests, the imaging and hormone levels in the body to ensure right hormonal diagnosis.
Personalized Treatment Plans: Treatment for endocrine system disorders usually involves hormone replacement therapy, use of drugs that modulate hormones or changes in a person’s lifestyle.
Ongoing Monitoring: Many hormonal situations are chronic in nature, and therefore their treatment may have to span a long period. Your endocrinologist will review your condition, make changes in the treatment if necessary and check that your hormonal levels are normal over time.
Holistic Care: When hormonal balance is disturbed, practically all aspects of a given individual’s physiology may be impacted. Endocrinologist thus, understand how endocrine functions and dysfunctions affect patients’ wellbeing, and how you can work with other professionals to address these issues.

